
Thermocouple and Thermoresistor Fault Handling (Part 1)
2025-09-05 09:47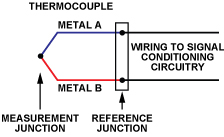
Temperature Detection Principle
Temperature is a physical quantity that characterizes the degree of coldness or heat of an object or a system. According to the fundamentals of molecular physics, temperature reflects the intensity of the random thermal motion of molecules within the object.
Methods and Classification of Temperature Measurement
The temperature detection methods can be classified into two major categories based on whether the sensitive element and the measured medium come into contact: contact-type and non-contact-type. The contact-type detection methods mainly include expansion-type temperature detection instruments based on the property that the volume of an object expands when heated; thermoresistive temperature detection instruments based on the change of resistance of conductors or semiconductors with temperature; and thermocouple temperature detection instruments based on the hot spot effect. The non-contact-type detection methods utilize the corresponding relationship between the thermal radiation characteristics of an object and its temperature to detect the temperature of the object, including the luminance method, the total radiation method, and the colorimetric method, etc.
2.1 According to the measurement method, they are divided into contact-type temperature measurement instruments and non-contact-type temperature measurement instruments.
1)Contact-type temperature meters are classified according to their measurement principles into expansion-type temperature meters (liquid column thermometers, bimetallic thermometers), pressure-type temperature meters (liquid, gas, and vapor temperature packages), resistance-type temperature meters (copper and platinum resistors), and thermoelectric potential-type temperature meters (nickel-chromium-nickel-silicon, nickel-chromium-conium, platinum-rhodium-platinum, etc. thermocouples).
2) Non-contact temperature meters are classified according to their working principles into radiation-type and infrared absorption-type temperature measuring instruments.
2.2 They are classified into four types in a fixed manner: flange fixed installation; threaded connection fixed installation; combined flange and threaded connection fixed installation; simple protective sleeve insertion installation.
1) Flange installation: On the equipment and the medium-pressure and low-pressure pipelines exposed to high-temperature corrosive media, it has wide adaptability, is conducive to corrosion prevention, and is convenient for maintenance.
2) Threaded connection fixation: For pipelines without corrosive media, it is small in size and compact in installation. For high-pressure pipelines, welded temperature gauge sleeves are used.
3) Flange and threaded connection for combined fixed installation: When an additional protective cover is worn, it is applicable for installation on pipelines and equipment exposed to corrosive media.
4) Simple protective cover insertion installation: Suitable for the temporary installation of rod-type thermometers on low-pressure pipelines for testing purposes.
Principles, Applications, Temperature Range and Accuracy of Thermocouples and Thermoresistors
1.What are the principles, applications, temperature range and accuracy of thermocouples? A thermocouple is composed of two different materials of metal wires forming a junction. When exposed to temperature changes, it generates an electric potential. The difference in electric potential between the two thermoelectric wires is the thermoelectric voltage. The millivolt is represented by mAV. This thermoelectric voltage is converted into temperature based on the material's properties. Various protective sleeves can be added as needed, and it can be used to measure temperatures in various media. Its measurement range is -40 to 1600 ℃, and the general accuracy is Class I 0.4%|t| and Class II 0.75%|t|.
2. Principles, applications, temperature range and accuracy of thermal resistors? The temperature measurement of thermal resistors is based on the characteristic that the resistance value of a metal conductor increases with the rise in temperature. Most thermal resistors are made of pure metal materials. Currently, the most commonly used ones are platinum and copper. Their temperature measurement range is -200 to 600℃, and the general accuracy is Class A ± (0.15 + 0.002|t|)℃, and Class B ± (0.3 + 0.005|t|)℃.
3. The temperature scale numbers of thermocouples are S, R, B, K, N, T, E, and J.
4. Classification of thermal resistors: Pt100, Pt10, Cu100, Cu50
5. The classification of junction boxes can generally be divided into small waterproof, waterproof, explosion-proof, multi-point, etc.; the materials include aluminum alloy, engineering plastic, stainless steel, cast iron, etc.; according to the protection level, they can be classified as: IP65 and IP68 junction boxes. The definitions of IP65 and 68 are: IP = protection. The first number 6 = no dust can enter, the second number 5 = protection against water jet, the second number 8 = protection against water immersion, and the immersion time and water pressure are determined according to customer requirements.
