
Common Faults of Differential Pressure Transmitter
2025-05-22 14:30
The differential pressure transmitter is a transmitter that measures the pressure difference between the two ends of the transmitter. Unlike general pressure transmitters, it has two input pressure interfaces, which are also divided into positive pressure end and negative pressure end. It can only be measured when the pressure of the positive pressure end is greater than the pressure of the negative pressure end. The principle of the differential pressure transmitter is that the isolation diaphragm on both sides of the transmitter sensor directly receives the differential pressure from the pressure pipes on both sides, and then transmits it to the measuring element through the sealing liquid in the diaphragm and converts the measured differential pressure signal into an electrical signal corresponding to it. Finally, it is transmitted to the converter and amplified and processed as a standard electrical signal output. As shown in the figure below:
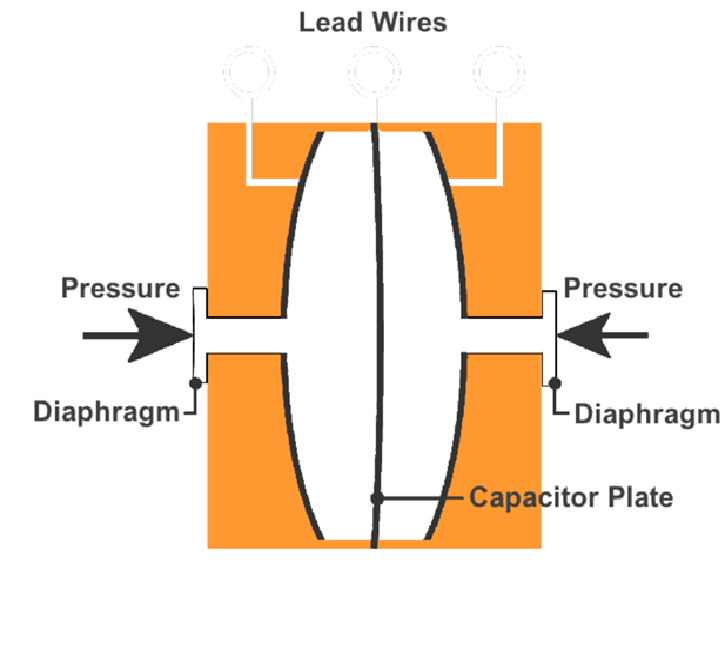
During the measurement process, the transmitter often has some faults. It is crucial for continuous production to timely determine, analyze and deal with faults in the production process. Based on the experience in daily instrument debugging, we have summarized some judgment methods and analysis methods.
1. Fault diagnosis
1) Investigation method: smoke, odor, lightning strike, misoperation, etc. before the fault occurs.
2) Intuitive method: observe the external damage of the measuring circuit, line shedding, leakage of the pressure pipe, overheating of the circuit and the status of the power switch, etc.
3) Detection method:
a. Open circuit detection: separate the suspected faulty part from other parts to check whether the fault disappears. If it disappears, determine the fault location. Otherwise, you can proceed to the next step. For example, if the intelligent differential pressure transmitter cannot communicate normally, the power supply can be disconnected from the meter body, and the transmitter can be powered on by adding another power supply on site to communicate, so as to check whether the electromagnetic signal superimposed on the cable interferes with the communication.
b. Short circuit detection: Under the condition of ensuring safety, short-circuit the relevant part of the circuit directly. For example, if the output value of the differential pressure transmitter is too small, the pressure pipe can be disconnected, and the differential pressure signal can be directly led from the primary pressure valve to both sides of the differential pressure transmitter. Observe the output of the transmitter to determine the connectivity of the blockage and leakage of the pressure pipe.
c. Replacement test: Replace the suspected faulty part to determine the faulty part. For example, if the transmitter circuit board is suspected to be faulty, a piece can be temporarily replaced to determine the cause.
d. Partial test: Divide the measurement circuit into several parts, such as power supply, signal output, signal transmission, and signal detection. Check the parts from simple to complex, from the outside to the inside, narrow the scope, and find the fault location.
2. Solutions to positive and negative migration faults of differential pressure transmitters
1) Positive migration fault of differential pressure transmitters
To determine whether the differential pressure transmitter with positive migration is accurate during field use, first close the positive and negative pressure measurement chambers of the three-valve group of the differential pressure transmitter, open the balance valve and the instrument vent plug, and the instrument output should be less than 4mA. If the output is not less than 4mA, it may be that the positive pressure chamber lead or the three-valve group is blocked. Secondly, close the pressure point of the positive pressure chamber and open the vent switch. The output should be 4mA. If the output is lower than 4mA, it may be that the migration amount has decreased or the zero position is low; if there is isolation fluid, it may be that the isolation fluid is not filled or leaked from somewhere else; if the output is higher than 4mA, it means that the migration amount has increased or the zero position is high.
2) Negative migration failure of differential pressure transmitter
To determine whether the differential pressure transmitter with negative migration is accurate during field use, first close the positive and negative pressure measurement chambers of the three-valve group of the differential pressure transmitter, open the balance valve and the instrument vent plug, and the instrument output should be 20mA. Secondly, close the pressure points of the positive and negative pressure chambers, and open the vent switch. At this time, the instrument output should be 4mA. If it is not 20mA or 4mA, check whether the positive and negative pressure chamber leads are blocked, whether the migration amount has changed, whether the zero position is accurate, whether the isolation fluid has been lost, etc.
